What do Buddhists eat?
What do Buddhists eat?
The practice of moderate eating
The Buddhist practice of frugal eating is based on the idea of minimizing food consumption and cultivating gratitude for food. This practice encourages Buddhists to adopt a vegetarian or vegan diet, and to avoid foods that can cause animal suffering. They also strive to eat fresh, unprocessed, sustainably sourced foods.
By embracing restrained eating, Buddhists learn to recognize the interconnectedness of all living things and cultivate kindness toward animals. Therefore, they avoid meat, dairy products and eggs, as they often require animal suffering. By adopting a plant-based diet, Buddhists also support environmental protection by reducing their carbon footprint.
Food eaten by Buddhists
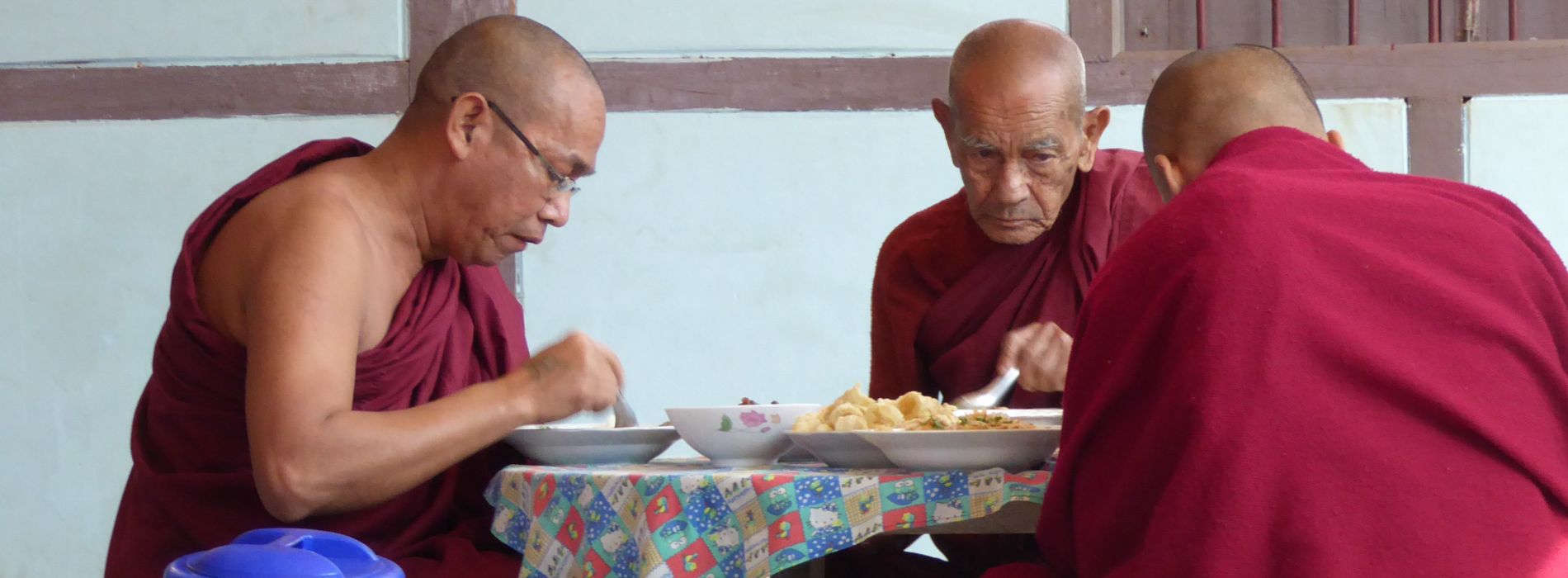
Buddhists consume a variety of foods that can be grouped into different categories: cereals, vegetables, fruits, legumes, nuts and seeds. They also emphasize the consumption of organic and seasonal products. By avoiding processed foods and artificial additives, they favor natural and whole foods.
Buddhists appreciate simple, balanced meals, prepared with love and conscience. They practice gratitude towards food by making offerings before eating and taking time to appreciate each bite. Slowness and mindfulness are important aspects of practicing sober eating.
Among the favorite foods of Buddhists, we find rice, green vegetables, legumes, nuts, seeds, fresh fruits and aromatic herbs. These foods provide balanced nutrition, promote health, and help cultivate compassion for all living things.
Fasting and meditation
Besides abstemious eating, Buddhists also practice fasting and meditation to purify the mind and body. Fasting is considered a beneficial practice for health and for developing mental discipline. It can be practiced in different ways, such as intermittent fasting or complete fasting for certain periods.
Meditation is also an important part of Buddhist practice. By meditating regularly, Buddhists cultivate self-awareness and mental clarity. This helps them make informed decisions about their diet and develop a harmonious relationship with food.
By combining restrained eating, fasting and meditation, Buddhists seek to cultivate compassion for all living beings, live in harmony with nature and cultivate inner peace.
Cultural influence on Buddhist diet
The practice of Buddhist diet varies according to different Buddhist cultures and traditions. For example, in countries where Buddhism is strongly rooted, such as Japan, China and Thailand, Buddhists have adopted specific dishes that reflect their local culture.
Japanese Zen Buddhism, for example, emphasizes the simplicity and seasonality of foods. Buddhist meals in Japan, called shōjin ryōri, consist of delicate, artistically presented vegetarian dishes. These meals are often served in Buddhist temples and during spiritual retreats.
Chinese vegetarian cuisine
In China, many Buddhists practice a form of vegetarianism known as Buddhist vegetarian cuisine. This cuisine uses meat substitutes made from soy, seitan (wheat), mushrooms and other plant-based ingredients to recreate the flavors and textures of traditional Chinese dishes. These dishes are often served during Buddhist celebrations and in temples.
Chinese vegetarian cuisine is known for its variety and complexity. It includes a large selection of vegetables, tofu, noodles, rice and aromatic sauces. Dishes are often carefully prepared and presented in an aesthetically pleasing manner.
In Thailand, Buddhists generally eat vegetarian during religious holidays, particularly during the Chinese Vegetarianism Festival. Vegetarian Thai dishes use a wide variety of herbs and spices to create bright, balanced flavors.
Buddhist diet for a healthy life
Beyond religious beliefs, the Buddhist diet can also be followed by people who wish to adopt a healthy and environmentally friendly lifestyle. By avoiding animal products and processed foods, you can improve your health and reduce the risk of diet-related illnesses.
By adopting a plant-based diet, you can increase your intake of fiber, vitamins and essential minerals. Plant foods are also often rich in antioxidants, healthy fatty acids, and health-promoting phytonutrients.
The health benefits of the Buddhist diet
Various studies have shown that plant-based diets can help prevent cardiovascular disease, diabetes, obesity and certain types of cancer. By avoiding processed food products and favoring whole, unrefined foods, we can reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
Buddhist eating also emphasizes practicing mindfulness during meals, which can contribute to better digestion, reduced stress, and greater food satisfaction.
In conclusion, the Buddhist diet is based on principles of sobriety, compassion towards animals and gratitude towards food. By adopting a vegetarian or vegan diet, practicing fasting and meditation, and respecting cultural traditions, Buddhists seek to cultivate a healthy life, in harmony with nature. nature and the living beings that surround us.