What is the spiritual guide of Buddhism?
The role of the Buddha in Buddhism
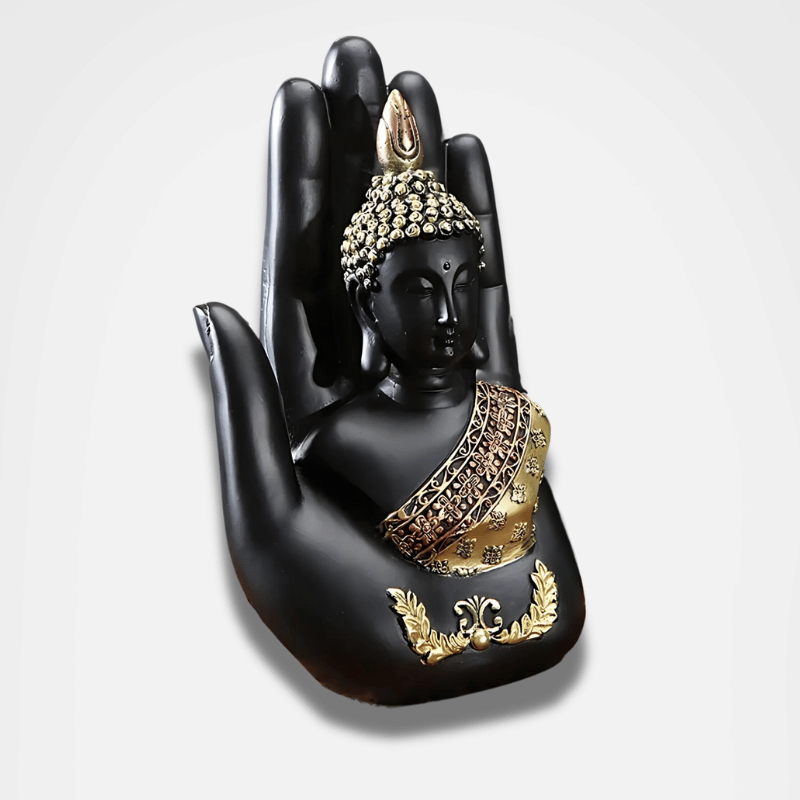
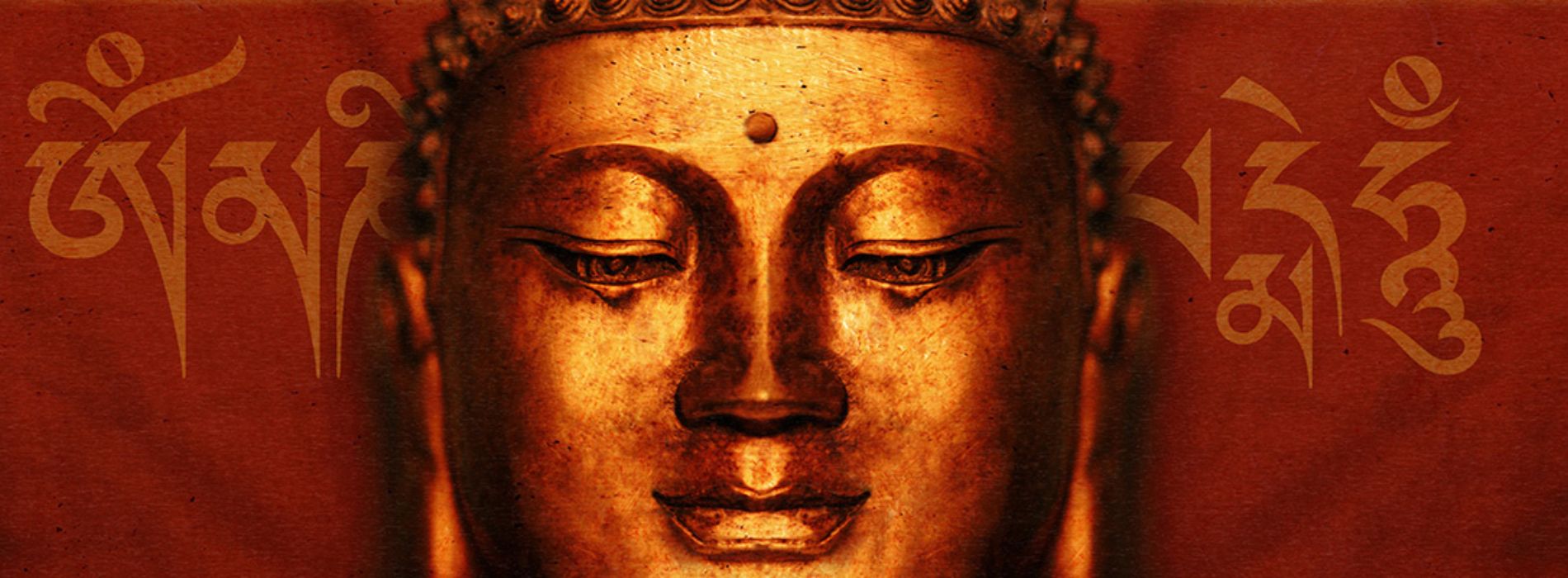
In Buddhism, the spiritual guide is known as the Buddha. The Buddha is considered to be one who has achieved ultimate enlightenment and who can guide others on the path to liberation. He is revered and respected as a spiritual teacher and role model. The Buddha is often represented by a statue seated in a meditation posture, with his hands placed one on top of the other in the gesture of meditation. His wisdom and compassion are extremely important qualities in the practice of Buddhism.
The Buddha taught the Four Noble Truths and the Noble Eightfold Path, which are the fundamental principles of Buddhism. These teachings guide practitioners on the path to liberation from suffering and the attainment of nirvana, the ultimate state of enlightenment.
Compassion in Buddhism
Compassion is one of the most important aspects of Buddhism. The Buddha taught that compassion toward all living beings is essential to achieving enlightenment. Compassion is feeling empathy and taking action to alleviate the suffering of others. In Buddhism, we practice compassion by developing loving-kindness towards all living beings, including ourselves. It means recognizing that all living beings seek happiness and want to avoid suffering, just as we do.
Compassion is cultivated through meditation and reflection on suffering and the impermanence of life. By practicing compassion, Buddhists hope to develop an altruistic attitude in all aspects of their lives and thereby contribute to world peace and happiness.
Compassion is also at the heart of bodhisattvas, who are beings who have reached an advanced level of spiritual awakening but who choose to give up their own nirvana to remain on Earth and help others to achieve awakening. Bodhisattvas are considered inspiring examples of compassion and benevolence for all Buddhist practitioners.
Meditation in Buddhism
Meditation is an essential practice in Buddhism. It plays a central role in the search for enlightenment and in the transformation of the mind. Meditation helps cultivate concentration, mental clarity and kindness towards oneself and others. It is often used to develop mindfulness, that is, the ability to remain aware and attentive in each present moment.
In Buddhism, there are different forms of meditation, such as sitting meditation, walking meditation, and breathing meditation. Each form of meditation has its own techniques and goals, but what they all have in common is developing attention and being present in the moment.
Regular meditation practice helps Buddhists develop a deeper understanding of the nature of mind and reality. It also helps cultivate compassion and wisdom, two essential qualities for achieving enlightenment.
The role of spiritual teachers in Buddhism
In addition to the Buddha, there are also other important spiritual teachers in Buddhism. These teachers are people who have reached a high level of spiritual awakening and who can guide others on the path to liberation. They are revered and considered sources of inspiration and wisdom for practitioners.
Spiritual teachers are usually called masters or gurus in Buddhism. They play a crucial role in the transmission of Buddhist teachings and practices. They guide practitioners on the path of meditation, mindfulness and inner transformation.
The relationship between spiritual teachers and disciples
The relationship between spiritual teachers and disciples is based on mutual respect and trust. Disciples look to teachers as preeminent guides on the path to enlightenment and seek to follow their examples and guidance. They place great importance on studying the teachings and practicing the meditations recommended by the teachers.
Spiritual teachers, for their part, undertake to guide disciples on the path to awakening by transmitting their experience and wisdom. They encourage them to develop their own understanding and to question the teachings critically. The relationship between teachers and disciples is therefore one of interaction and mutual learning.
It is important for Buddhist practitioners to find a spiritual teacher who is suited to their needs and spiritual aspirations. They may seek out teachers at meditation centers or Buddhist monasteries, or receive teachings through books, online courses, or other media.
Lineages of transmission in Buddhism
Buddhism is marked by a tradition of transmission lineages, which are chains of transmission of teachings and practices from a teacher to a disciple. These lines of transmission are considered a guarantee of the authenticity of the teachings and the continuity of Buddhist practice.
There are different lineages of transmission in Buddhism, often dating back to the teachings and practices of the Buddha's first disciples. Each lineage has its own specific traditions and practices, but they all share the same goal of guiding practitioners on the path to awakening.
Practitioners can choose to receive the teachings and initiations of one or more transmission lineages, depending on their spiritual affinities and their aspiration to achieve enlightenment.
The importance of community in Buddhism
The community plays a central role in the practice and understanding of Buddhism. Buddhists meet regularly as a group to meditate, study the teachings, participate in rituals, and support each other's spiritual practice.
Community can take many forms, from an informal meditation group to an organized monastic community. It provides a space where members can support each other, share experiences and learn from each other.
The advantages of community practice
Community practice has many benefits for Buddhists. It helps cultivate compassion and kindness towards other members of the community. By sharing their experiences and reflections, practitioners can deepen their understanding of the teachings and develop their personal practice.
The community also provides emotional and social support to practitioners. There are often moments of sharing and exchange during meditation sessions or study circles, where members can talk openly about their difficulties and receive advice and support.
Finally, the community is a place where Buddhist rituals and celebrations can be practiced collectively. These occasions provide community members with the opportunity to connect with Buddhist teachings and practices in a deeper and more meaningful way.
Personal practice and community
Personal practice is also essential in Buddhism. Buddhists are encouraged to meditate and study the teachings on a regular basis, outside of community gatherings. Personal practice helps cultivate mindfulness and compassion in daily life.
However, personal practice does not replace community. The community plays a complementary role in providing support, resources and opportunities to connect with other practitioners. Personal practice and community practice mutually reinforce and complement each other in the search for awakening and liberation.
Conclusion
Buddhism is a rich and complex spiritual tradition, based on the teachings of the Buddha and the practice of meditation and compassion. The spiritual guide in Buddhism is the Buddha himself, but there are also other important spiritual teachers in the Buddhist tradition. The community also plays a vital role in the practice and understanding of Buddhism, providing support, resources and opportunities for sharing and learning. Whether through meditation, compassion or community practice, Buddhism offers multiple paths to achieving awakening and liberation from suffering.
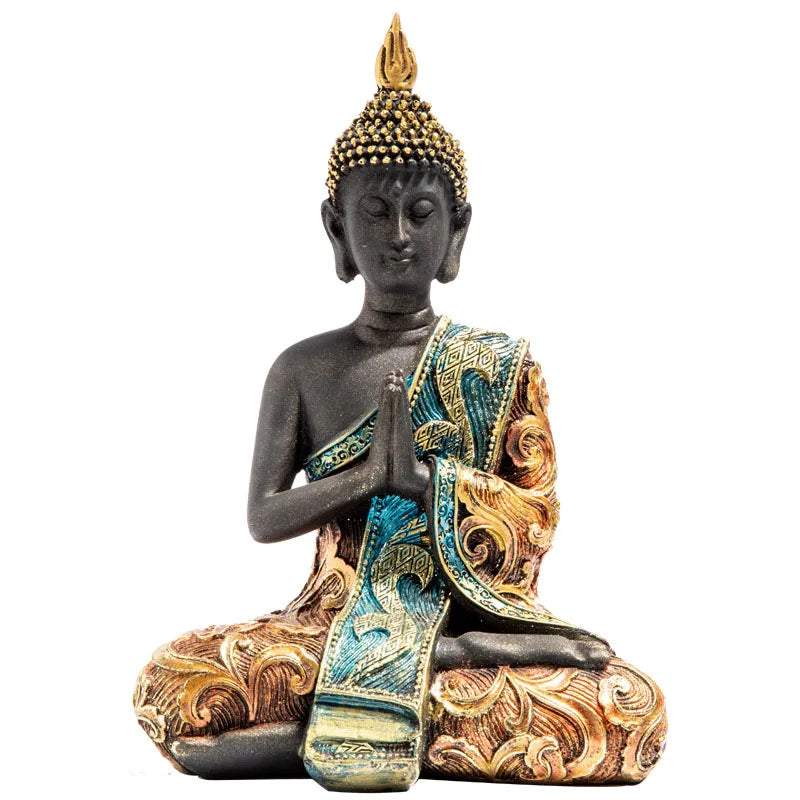












































1 comment
Deborah Smith
Thank u 4 this info. However, I still don’t know who to identify as my spiritual guide. Is it Geshe Kelsang Gyatsu Rinpoche or Je Tsongkapa or Dorje Shugden. Very confused.